The Metal Injection Molding (MIM) process can produce a wide variety of structural materials that are common in military, medical, automotive, industrial, and aerospace applications. Metal injection molding's raw material is called feedstock. Feedstock is a mixture of powder metal and polymer specifically blended to create different metal parts.
Metal Injection Molding materials have been designed to achieve high densities, withstand the complex debinding and sintering process. Our materials also mirror alloys developed for wrought products. The availability of metal powders facilitates the formulation of modified MIM alloys designed for specific applications.
APP Material Expertise
Material selection is a vital step in the design process. If you want your final product to outperform the competition, APP has got you covered. We offer:
- Onsite P.E Metallurgist and Material Scientists/Engineers
- Ability to manufacture customized feedstocks in-house
- Technical guidance for selecting powders
- Intellectual property development
- Fast reaction time for alloy/shrink modification
- Mechanical properties exceeding MPIF Standard 35
- Ability to process BASF/Catamold® Feedstock
- Diverse alloy selection from same tool
- In-house metallurgy carbon testing
Metal Powder Feedstock
Metal injection molding feedstock is manufactured by mixing fine metal powder with waxes and polymers to create the foundation to what will become the MIM part. Pelletized Feedstock is then injected into the molding machines and molds to create a green part.
APP has the unique ability to formulate and manufacture proprietary metal powder feedstock specifically designed for our metal injection molding process. Backed metallurgical science, the mechanical properties of mim materials developed by APP meet and exceed MPIF Standard 35 properties.
Our metallurgical expertise also gives us the ability to process off-the-shelf BASF/ Catamold® feedstock. The capability to process both in-house and off-the-shelf feedstock, gives the customer the ability to seamlessly transfer a mold developed with a competitor's process.
MIM Alloys
Engineers turn to metal injection molding because of the many material options available. APP manufactures and stocks a variety of alloys such as low-alloy steels, stainless steels, tool steels, soft-magnetic steels, and tungsten. The table below is an overview of available MIM materials, applications, and features.
| Material Family |
Application |
Specific Alloys |
Specific Feature |
| Stainless Steel |
Medical, electronic, hardware, sporting goods, aerospace, consumer products |
| 17-4PH |
| 316L |
| 420, 440C |
| 310 |
|
| Strength, heat treatable |
| Corrosion resistance, ductility, nonmagnetic |
| Hardness, wear resistance, heat treatable |
| Corrosion and heat resistance |
|
| Low-alloy Steel |
Hardware, bearings, races, consumer goods, machine parts |
| 1000 Series |
| 4000 Series |
| 52100 |
|
| Case hardenable |
| General purpose |
| High wear resistance |
|
| Tool Steel |
Wood and metal cutting tools |
|
| 61-66 HRC |
| 63-68 HRC |
| 65-70 HRC |
| 55-60 HRC |
|
| Bioimplantable |
Implantable, Prosthetic replacements (hips, knees, etc.) bone plates, screws, rods, heart valves |
| F-75 (ASTM F2886) |
| MP35N (ASTM F562) |
|
| High strength, superior corrosion resistance, non-magnetic, biocompatibility |
|
| Titanium |
Medical, aerospace, consumer products |
|
| Light Weight |
| Light weight, high strength |
|
| Copper |
Electronic, thermal management |
|
| High thermal and electrical conductivity |
| High thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion |
|
| Magnetic |
Electronic solenoids, armatures, relay |
| Fe-3%Si |
| Fe-50%Ni |
| Fe-50%Co |
|
| Low core losses and high electrical resistivity |
| High permeability and low coercive field |
| Highest magnetic saturation |
|
| Tungsten |
Military, electronic, sporting goods |
|
| Density |
| Density and toughness |
|
| Hardmetals |
Cutting and wear applications |
|
| Higher hardness |
| Higher toughness |
|
MIM STAINLESS STEELS*
As a leader in metal injection molding for the last 20 years, we pride ourselves on our material expertise. This guide walks you through typical material properties for MIM stainless steels. Need help choosing the best option? Let our application experts take a closer look. Call us at 814-342-5895 or email us at engineer@4-app.com
Features And Applications
| Microstructure |
Grade |
Alloy Features |
Applications |
| Precipitation Hardening |
17-4PH |
Strength, Heat Treatable, Corrosion Resistance
| Firearms, Medical Devices (mechanical joints, suturing saws, wound forceps), Hand & Power Tools, Sporting Goods, Electronics, Aerospace, Automotive, Fiber Optic Connectors, and Consumer Goods. |
| Austenitic |
316L |
Superior Corrosion Resistance, Ductility, Non-magnetic |
| Martensitic |
420, 440C |
Hardness, Wear Resistance, Heat Treatable |
| Ferritic |
430L |
Magnetic Stainless Steel with Resistance to Atmospheric Corrosion and General Oxidation |
Alloy Composition
| Element |
MIM 17-4PH SS |
MIM 316L |
MIM 420 |
MIM 440 |
MIM 430L |
| C |
0.07 max |
.03 max |
.15-.4 |
.9-1.25 |
.05 (max) |
| Si |
1.0 max |
1.0 max |
1.0 max |
1.0 max |
1.0 max |
| Cr |
15.5-17.5 |
16-18 |
12-14 |
16-18 |
16-18 |
| Mo |
- |
2-3 |
- |
.75 max |
- |
| Mn |
1.0 max |
2.0 max |
1.0 max |
1.0 max |
1.0 max |
| Fe |
Bal. |
Bal. |
Bal. |
Bal. |
Bal. |
| Ni |
3-5 |
10-14 |
- |
.6 max |
- |
| Cu |
3-5 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| Nb |
0.15-0.45 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Typical Material Properties
| Material |
Density (g/cm3) |
YS (MPa) |
UTS (MPa) |
Elongation (%) |
Unnotched Charpy impact energy (J) |
Macro Hardness |
Young's Modulus (GPa) |
| MIM 17-4 PH |
7.6 |
740 |
900 |
6 |
100 |
27-32 HRC |
190 |
| MIM 17-4 PH (H900) |
7.6 |
1100 |
1200 |
4 |
100 |
38-42 HRC |
190 |
| MIM 316L |
7.6 |
180 |
520 |
40 |
140 |
67 HRB |
190 |
| MIM 420 (heat treated) |
7.4 |
1200 |
1370 |
- |
30 |
44 HRB |
190 |
| MIM 440 (heat treated) |
7.5 |
1600 |
1250 |
1 |
4 |
55 HRC |
190 |
| MIM 430L |
7.5 |
230 |
410 |
25 |
110 |
65 HRB |
190 |
Download PDF
MIM LOW-ALLOY STEELS*
As a leader in metal injection molding for the last 20 years, we pride ourselves on our material expertise. This guide walks you through typical material properties for MIM low-alloy steels. Low-alloy steels exhibit superior mechanical properties to plain carbon steels due to the addition of alloying elements. MIM low-carbon steels can achieve higher densities and greater mechanical properties over castings. Need help choosing the best option? Let our application experts take a closer look. Call us at 814-342-5895 or email us at engineer@4-app.com
Features And Applications
| Grade |
Alloy Features |
Applications |
| 2200, 2700, 8620, 9310 |
Case Hardenable |
Firearms, Consumer Goods, General, Industrial, Wood and Metal Cutting |
| 400 Series |
General Purpose |
| 52100 |
High Wear Resistance |
Alloy Composition
| Element |
MIM 4605 |
MIM 4140 |
MIM 4340 |
MIM 2700 (FN08) |
MIM 2200 (Fe-2Ni) |
MIM 52100 |
MIM 8620 |
MIM 9310 |
MIM 430L |
| C |
.4-.6 |
.3-.5 |
.3-.5 |
.1 max |
.1 max |
.8-1.2 |
.15-.23 |
.2 max |
.05 (max) |
| Si |
1.0 max |
.6 max |
.5 max |
1.0 max |
1.0 max |
- |
1.0 max |
- |
1.0 max |
| Cr |
- |
.8-1.2 |
.6-1.2 |
- |
- |
1.3-1.6 |
.4-.6 |
.3-.8 |
16-18 |
| Mo |
.2-.5 |
.2-.3 |
.5 max |
.5 max |
.5 max |
- |
.15-.25 |
.1-.25 |
- |
| Mn |
- |
1.0 max |
.8 max |
- |
- |
.25-.45 |
.7-.9 |
- |
1.0 max |
| Fe |
Bal. |
Bal. |
Bal. |
Bal. |
Bal. |
Bal. |
Bal. |
Bal. |
Bal. |
| Ni |
1.5-2.5 |
- |
1.25-2.0 |
6.5-8.5 |
1.5-2.5 |
- |
.4-.7 |
2.5-3.5 |
- |
| Cu |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
.025 max |
.035 max |
.025 max |
- |
| Nb |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
.025 max |
.040 max |
.025 |
- |
Typical Material Properties
| Material |
Density (g/cm3) |
YS (MPa) |
UTS (MPa) |
Elongation (%) |
Unnotched Charpy impact energy (J) |
Macro Hardness |
Case Hardened |
Young's Modulus (GPa) |
| MIM 4605 HT |
7.55 |
1480 |
1650 |
1 |
55 |
43-48 HRC |
- |
210 |
| MIM 4140 HT |
7.5 |
1200 |
1600 |
5 |
75 |
43-48 HRC |
- |
200 |
| MIM 4340 HT |
7.5 |
1100 |
1200 |
6 |
- |
40-45 |
- |
- |
| MIM 2700 |
7.6 |
250 |
400 |
12 |
175 |
69 HRB |
50-56 HRC |
190 |
| MIM 2200 |
7.6 |
125 |
280 |
35 |
135 |
45 HRB |
56-62 HRC |
190 |
| MIM 51200 HT |
7.5 |
1100 |
1500 |
2 |
- |
55-62 HRC |
- |
- |
| MIM 8620 |
7.5 |
130 |
320 |
25 |
- |
100 HRB |
- |
- |
| MIM 9310 |
7.5 |
350 |
540 |
15 |
- |
375 HV1 |
56-62 HRC |
- |
Download PDF
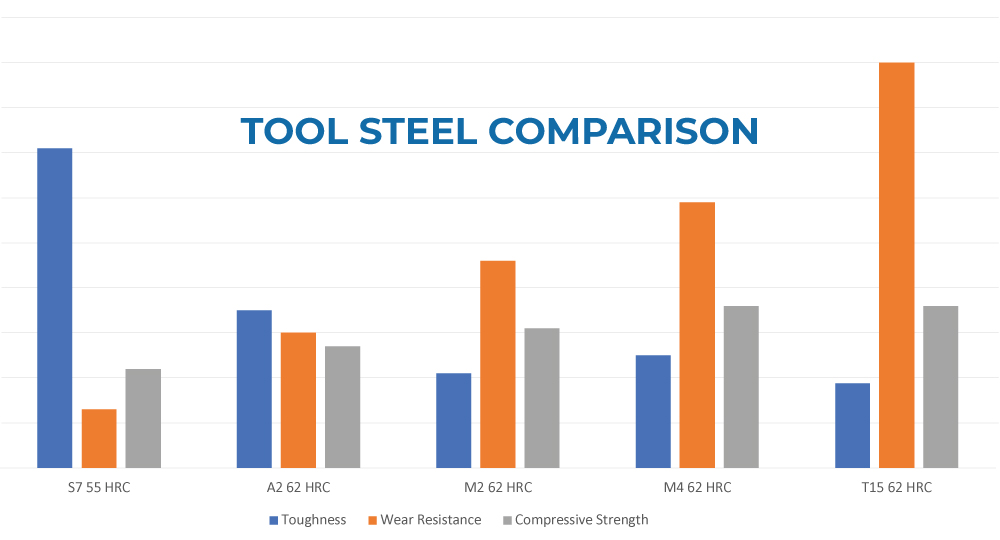
MIM TOOL STEELS*
As a leader in metal injection molding for the last 20 years, we pride ourselves on our material expertise. This guide walks you through typical material properties for MIM Tool Steels. Tool steels are a family of steels that contain dispersed carbides in a hardened steel matrix. These steels are used in high impact, metal cutting, and many other hot and cold wear applications. Need help choosing the best option? Let our application experts take a closer look. Call us at 814-342-5895 or email us at engineer@4-app.com
Features And Applications
| Grade |
Hardness |
Alloy Features |
Applications |
| S7 |
55-60 HRC |
High Impact Resistance, High Toughness |
Firearms, Consumer Goods, General Industrial, Cutting Tools. |
| A2 |
60-65 HRC |
Good Toughness, Moderate Wear Resistance |
| M2/M4 |
60-65 HRC |
Very Good Wear Resistance, Good Toughness |
| T15 |
60-65 HRC |
Extremely Good Wear Resistance |
Alloy Composition
| Alloy |
C |
Mn |
Si |
Cr |
W |
V |
Ni |
Mo |
Co |
Cu |
Fe |
| MIM S7 |
.45 - .65 |
.9 max |
.2 - 1.0 |
3.0 - 3.5 |
- |
- |
- |
1.3 - 1.8 |
- |
- |
Bal |
| MIM A2 |
.95 - 1.05 |
1.00 max |
.5 max |
4.75 - 5.5 |
- |
.15 - .5 |
- |
.9 - 1.4 |
- |
- |
Bal |
| MIM M2 |
.8 - 0.9 |
- |
- |
3.5 - 4.5 |
5.5 - 6.5 |
1.5 - 2.2 |
- |
4.5 - 5.5 |
- |
- |
Bal |
| MIM M4 |
1.25 - 1.4 |
.15 - .4 |
.2 - .45 |
3.75 - 4.75 |
5.25 - 6.65- |
3.75 - 4.5 |
- |
4.25 - 5.5 |
- |
- |
Bal |
Typical Material Properties
| Material |
Density (g/cm3) |
YS (MPa) |
UTS (MPa) |
Elongation (%) |
Unnotched Charpy impact energy (J) |
Macro Hardness |
Case Hardened |
Young's Modulus (GPa) |
| MIM S7 HT |
7.4 |
1550 |
1750 |
2 |
- |
45-53 HRC |
- |
- |
| MIM A2 HT |
7.5 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
55-63 HRC |
- |
- |
| MIM M2 HT |
7.9 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
55-65 HRC |
- |
- |
| MIM M4 HT |
7.9 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
60-65 HRC |
- |
- |
| MIM T15 HT |
8.2 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
60-65 HRC |
- |
- |
 Download PDF
Download PDF
BIOIMPLANTABLE ALLOYS*
As a leader in metal injection molding for the last 20 years, we pride ourselves on our material expertise. This guide
walks you through typical material properties for Bioimplantable Alloys. Bioimplantable Alloys are a family of Cobalt-chromium alloys commonly used for the implantation of MIM components in the medical device and orthopedic industry. Need help choosing the best option? Let our application experts take a closer look. Call us at 814-342-5895 or email us at engineer@4-app.com.
Features And Applications
| Grade |
Hardness |
Alloy Features |
Applications |
| F-75 (ASTM F2886) |
25 HRC |
High strength, superior corrosion resistance, non-magnetic, biocompatibility |
Prosthetic replacements (hips, knees, etc.) bone plates, screws, rods, heart valves |
| MP35N (ASTM F562) |
8 HRC |
Alloy Composition
| Alloy |
C |
Mn |
Si |
Cr |
W |
V |
Ni |
Mo |
Co |
Cu |
Fe |
| MIM F-75 |
0.35 Max |
1.00 max |
- |
27-30 |
- |
- |
0.50 Max |
5-7 |
Bal |
- |
0.75 Max |
| MIM MP35N |
0.025 Max |
0.15 Max |
- |
19-21 |
- |
- |
33-37 |
.9 - 10.5 |
Bal |
- |
1.00 max |
Typical Material Properties
| Material |
Density (g/cm3) |
YS (MPa) |
UTS (MPa) |
Elongation (%) |
Unnotched Charpy impact energy (J) |
Macro Hardness |
Young's Modulus (GPa) |
| MIM F-75 - Hipped |
7.8 |
520 |
1000 |
40 |
- |
25 HRC |
190 |
| MIM MP35N |
8.3 |
400 |
900 |
10 |
- |
8 HRC |
- |
Comparison of MIM F75 and Cast F75
| Material |
YS (MPa) |
UTS (MPa) |
Elongation (%) |
Reduction in Area (%) |
Macro Hardness |
| MIM F-75 |
520 |
1000 |
40 |
25 |
25 HRC |
| MIM F-75 Minimum (ASTM F2886) |
480 |
825 |
10 |
10 |
- |
| Cast F-75 Typical |
550 |
880 |
16 |
18 |
25-35 HRC |
| Cast F-75 Minimum |
450 |
665 |
8 |
8 |
25-35 HRC |
Download PDF